Obesity promotes the expansion of metastasis-initiating cells in breast cancer
- Bousquenaud, Mélanie Experimental and Translational Oncology Laboratory, Division of Pathology, Department of Oncology, Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Science and Medicine, University of Fribourg, Fribourg, Switzerland
- Fico, Flavia Tumor Ecology, Laboratory, Division of Pathology, Department of Oncology, Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Science and Medicine, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Solinas, Giovanni Department of Molecular and Clinical Medicine, The Wallenberg Laboratory, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
- Rüegg, Curzio Experimental and Translational Oncology Laboratory, Division of Pathology, Department of Oncology, Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Science and Medicine, University of Fribourg, Fribourg, Switzerland - Swiss Integrative Center for Human Health, Fribourg, Switzerland
- Santamaria-Martínez, Albert Tumor Ecology, Laboratory, Division of Pathology, Department of Oncology, Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Science and Medicine, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
-
04.09.2018
Published in:
- Breast Cancer Research. - 2018, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 104
English
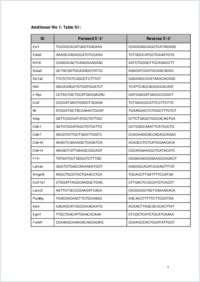
Obesity is a strong predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer, especially in postmenopausal women. In particular, tumors in obese patients tend to seed more distant metastases, although the biology behind this observation remains poorly understood.Methods: To elucidate the effects of the obese microenvironment on metastatic spread, we ovariectomized C57BL/6 J female mice and fed them either a regular diet (RD) or a high-fat diet (HFD) to generate a postmenopausal diet-induced obesity model. We then studied tumor progression to metastasis of Py230 and EO771 grafts. We analyzed and phenotyped the RD and HFD tumors and the surrounding adipose tissue by flow cytometry, qPCR, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and western blot. The influence of the microenvironment on tumor cells was assessed by performing cross-transplantation of RD and HFD tumor cells into other RD and HFD mice. The results were analyzed using the unpaired Student t test when comparing two variables, otherwise we used one-way or two-way analysis of variance. The relationship between two variables was calculated using correlation coefficients.Results: Our results show that tumors in obese mice grow faster, are also less vascularized, more hypoxic, of higher grade and enriched in CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils. Collectively, this favors induction of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and progression to claudin-low breast cancer, a subtype of triple-negative breast cancer that is enriched in cancer stem cells. Interestingly, transplanting HFD- derived tumor cells in RD mice transfers enhanced tumor growth and lung metastasis formation.Conclusions: These data indicate that a pro-metastatic effect of obesity is acquired by the tumor cells in the primary tumor independently of the microenvironment of the secondary site.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Médecine 3ème année, Département de Médecine
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Biological sciences
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 323466
- DOI 10.1186/s13058-018-1029-4
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/307469
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 188
File downloads:
- pdf: 310
- Supplementary material: 171