Plasma-functionalized electrospun matrix for biograft development and cardiac function stabilization
- Guex, Anne Géraldine Empa, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology, St. Gallen, Switzerland - Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University Hospital and University of Bern, Switzerland - Graduate School for Cellular and Biomedical Sciences, University of Bern, Switzerland
- Frobert, A. Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Valentin, Jeremy Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Fortunato, G. Empa, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology, St. Gallen, Switzerland
- Hegemann, D. Empa, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology, St. Gallen, Switzerland
- Cook, Stéphane Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Carrel, Thierry P. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University Hospital and University of Bern, Switzerland
- Tevaearai, H.T. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University Hospital and University of Bern, Switzerland
- Giraud, Marie-Noëlle Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
-
14.02.2014
Published in:
- Acta Biomaterialia. - 2014, vol. 10, no. 7, p. 2996–3006
Cardiac tissue engineering
In vivo functional evaluation
Electrospinning
Plasma polymerization
Echocardiography cell therapy
English
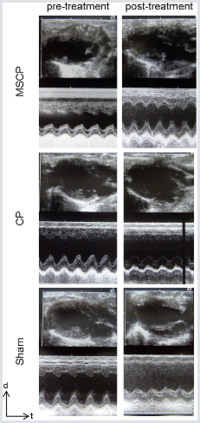
Cardiac tissue engineering approaches can deliver large numbers of cells to the damaged myocardium and have thus increasingly been considered as a possible curative treatment to counteract the high prevalence of progressive heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI). Optimal scaffold architecture and mechanical and chemical properties, as well as immune- and bio-compatibility, need to be addressed. We demonstrated that radio-frequency plasma surface functionalized electrospun poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL) fibres provide a suitable matrix for bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) cardiac implantation. Using a rat model of chronic MI, we showed that MSC-seeded plasma-coated PCL grafts stabilized cardiac function and attenuated dilatation. Significant relative decreases of 13% of the ejection fraction (EF) and 15% of the fractional shortening (FS) were observed in sham treated animals; respective decreases of 20% and 25% were measured 4 weeks after acellular patch implantation, whereas a steadied function was observed 4 weeks after MSC-patch implantation (relative decreases of 6% for both EF and FS).
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Médecine 3ème année
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Medicine
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 211459
- DOI 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.01.006
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/303542
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 118
File downloads:
- pdf: 315
- Supplementary material: 125