Physiological Response to the COVID-19 Vaccine: Insights From a Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blinded, Crossover Trial
PSPE
- Markovic, Andjela ORCID Department of Psychology, University of Fribourg, Switzerland. Department of Social Neuroscience and Social Psychology, Institute of Psychology, University of Bern, Switzerland. Department of Pulmonology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland. Ava Aktiengesellschaft (AG), Zurich, Switzerland
- Kovacevic, Vladimir ORCID Ava Aktiengesellschaft (AG), Zurich, Switzerland. The Institute for Artificial Intelligence Research and Development of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia
- Brakenhoff, Timo ORCID Julius Clinical, Zeist, Netherlands
- Veen, Duco ORCID Department of Methodology & Statistics, Utrecht University, Netherlands.Optentia Research Programme, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
- Klaver, Paul ORCID Julius Clinical, Zeist, Netherlands
- Mitratza, Marianna ORCID Julius Global Health, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center, Utrecht, Netherlands
- Downward, George ORCID Julius Global Health, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center, Utrecht, Netherlands
- Grobbee, Diederick ORCID Julius Global Health, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center, Utrecht, Netherlands
- Cronin, Maureen ORCID Ava Aktiengesellschaft (AG), Zurich, Switzerland
- Goodale, Brianna ORCID Ava Aktiengesellschaft (AG), Zurich, Switzerland.Julius Clinical, Zeist, Netherlands
- 2024
Published in:
- Journal of Medical Internet Research. - JMIR Publications Inc.. - 2024, vol. 26, p. 1-13
Wearable technology
Biosignals
Digital health
SARS-CoV-2
Vaccine reactogenicity
Menstrual cycle
Vaccine
Wearables
Sex
Development
Implementation
Medical device
Breathing rate
Heart rate
Biological mechanism
Immune response
Vaccination
English
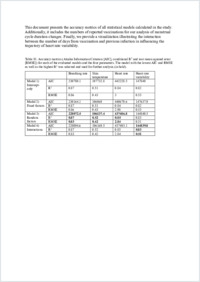
Background: Rapid development and implementation of vaccines constituted a crucial step in containing the COVID-19 pandemic. A comprehensive understanding of physiological responses to these vaccines is important to build trust in medicine. Objective: This study aims to investigate temporal dynamics before and after COVID-19 vaccination in 4 physiological parameters as well as the duration of menstrual cycle phases. Methods: In a prospective trial, 17,825 adults in the Netherlands wore a medical device on their wrist for up to 9 months. The device recorded their physiological signals and synchronized with a complementary smartphone app. By means of multilevel quadratic regression, we examined changes in wearable-recorded breathing rate, wrist skin temperature, heart rate, heart rate variability, and objectively assessed the duration of menstrual cycle phases in menstruating participants to assess the effects of COVID-19 vaccination. Results: The recorded physiological signals demonstrated short-term increases in breathing rate and heart rate after COVID-19 vaccination followed by a prompt rebound to baseline levels likely reflecting biological mechanisms accompanying the immune response to vaccination. No sex differences were evident in the measured physiological responses. In menstruating participants, we found a 0.8% decrease in the duration of the menstrual phase following vaccination. Conclusions: The observed short-term changes suggest that COVID-19 vaccines are not associated with long-term biophysical issues. Taken together, our work provides valuable insights into continuous fluctuations of physiological responses to vaccination and highlights the importance of digital solutions in health care.
- Faculty
- Faculté des lettres et des sciences humaines
- Department
- Département de Psychologie
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Psychology
- License
- Open access status
- gold
- Identifiers
-
- DOI 10.2196/51120
- ISSN 1438-8871
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/329190
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 126
File downloads:
- markovicetal-2024-covid-red: 93
- jmir_v26i1e51120_app1: 62