S-methyl methanethiosulfonate: promising late blight inhibitor or broad range toxin?
- Joller, Charlotte Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- Vrieze, Mout De Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- Moradi, Aboubakr Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- Fournier, Claudine Medical and Molecular Microbiology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- Chinchilla, Delphine Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- L'Haridon, Floriane Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- Bruisson, Sébastien Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
- Weisskopf, Laure Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, 1702 Fribourg, Switzerland
-
22.06.2020
Published in:
- Pathogens. - 2020, vol. 9, no. 6, p. 496
English
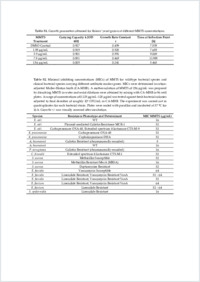
(1) Background: S-methyl methanethiosulfonate (MMTS), a sulfur containing volatile organic compound produced by plants and bacterial species, has recently been described to be an efficient anti-oomycete agent with promising perspectives for the control of the devastating potato late blight disease caused by Phytophthora infestans. However, earlier work raised questions regarding the putative toxicity of this compound. To assess the suitability of MMTS for late blight control in the field, the present study thus aimed at evaluating the effect of MMTS on a wide range of non- target organisms in comparison to P. infestans. (2) Methods: To this end, we exposed P. infestans, as well as different pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungi, bacteria, the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as well as the plant Arabidopsis thaliana to MMTS treatment and evaluated their response by means of in vitro assays. (3) Results: Our results showed that fungi (both mycelium and spores) tolerated MMTS better than the oomycete P. infestans, but that the compound nevertheless exhibited non-negligible toxic effects on bacteria, nematodes and plants. (4) Conclusions: We discuss the mode of action of MMTS and conclude that even though this compound might be too toxic for chemical application in the field, its strong anti-oomycete activity could still be exploited when naturally released at the site of infection by plant-associated microbes inoculated as biocontrol agents.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Département de Biologie
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Biological sciences
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 328905
- DOI 10.3390/pathogens9060496
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/309055
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 150
File downloads:
- pdf: 227
- Supplementary material: 164