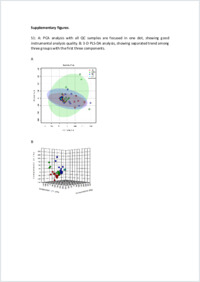
Alpha‐synuclein dopaminylation presented in plasma of both healthy subjects and parkinson’s disease patients
- Zhao, Huiyuan Section of Medicine University of Fribourg Fribourg CH1700 Switzerland - Division of Biological Technology, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Science Dalian China 116023
- Huang, Shuai Division of Biological Technology, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Science Dalian China 116023
- Palanisamy, Sivakumar Division of Biological Technology, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Science Dalian China 116023
- Wang, Cui Department of Neurology Dalian Central Hospital Dalian China 116033
- Rainer, Gregor Section of Medicine University of Fribourg Fribourg CH1700 Switzerland
- Zhang, Xiaozhe Division of Biological Technology, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Science Dalian China 116023
-
15.06.2020
Published in:
- PROTEOMICS – Clinical Applications. - 2020, vol. 14, no. 5, p. 1900117
English
Alpha‐synuclein (α‐syn) dopaminylation can lead to the death of dopaminergic neurons in the brain and is a risk factor of Parkinson's disease (PD). This study aims to examine whether such a posttranslational modification (PTM) is presented in human blood plasma. Experimental Design: In vitro reaction simulation between α‐syn and dopamine (DA) is conducted to study the biochemical mechanism. Then α‐syn from human blood plasma samples is detected by using immunoprecipitation‐mass spectrometry (IP‐MS). Lastly the levels of endogenous α‐syn and α‐syn dopaminylation in 88 blood plasma samples from patients with PD, major depressive disorder (MDD), and healthy control (HC) are compared. Results: DA modifies α‐syn with the addition of dopamine‐quinone (DAQ) into lysine sites of α‐syn in vitro and the addition of DAQ and 3,4‐dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL) in plasma samples. The unmodified α‐syn between the PD and HC groups showed similar levels. The levels of two peptides, one with lysine 34 (34K) DAQ modification and the other with lysine 23 (23K) ubiquitination, are significantly higher in PD and MDD compared with HC. Conclusions and Clinical Relevance: Thus, α‐syn dopaminylation is measurable and might be used to indicatethe presence and progression of neurological disorders.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Département de Médecine
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Biological sciences
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 329632
- DOI 10.1002/prca.201900117
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/308989
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 110
File downloads:
- pdf: 323
- Supplementary material: 147