Assessing meso- and microplastic pollution in the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian Seas
- Caldwell, Jessica Adolphe Merkle Institute, Université de Fribourg, Switzerland
- Petri-Fink, Alke Adolphe Merkle Institute, Université de Fribourg, Switzerland - Department of Chemistry, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Rothen-Rutishauser, Barbara Adolphe Merkle Institute, Université de Fribourg, Switzerland
- Lehner, Roman Adolphe Merkle Institute, Université de Fribourg, Switzerland - Sail and Explore Association, Ennenda, Switzerland
-
01.12.2019
Published in:
- Marine Pollution Bulletin. - 2019, vol. 149, p. 110572
English
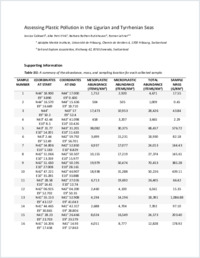
As the production of plastic products continues to increase, determining the fate of plastic waste in the environment is of high importance. Densely populated areas, such as Mediterranean coastlines, represent locations of high pollution risk for surrounding environments. Thus, this study aims to assess the abundance, size, and composition of floating meso- and microplastics collected during four weeks in 2018 in the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian Seas. The results show average meso- and microplastic particle concentrations of 28,376 ± 28,917 particles km−2, and an average mass of 268.61 ± 421.18 g km−2. The particle shape ratio was 65% fragments, 19% films, 10% lines, 4% foams, and 2% pellets. Microplastic particles comprised 65% of the sample. Analysis with attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy showed predominant polymer types included polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyamide. These data are an important starting point for long-term monitoring of plastic pollution levels within this region.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Département de Chimie, AMI - Bio-Nanomatériaux
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Chemistry
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 327952
- DOI 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110572
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/308245
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 125
File downloads:
- pdf: 288
- Supplementary material: 137