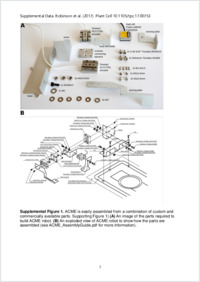
An automated confocal micro-extensometer enables in vivo quantification of mechanical properties with cellular resolution
- Robinson, Sarah Institute of Plant Sciences, University of Bern, Switzerland
- Huflejt, Michal Institute of Plant Sciences, University of Bern, Switzerland
- Barbier de Reuille, Pierre Institute of Plant Sciences, University of Bern, Switzerland
- Braybrook, Siobhan A. Sainsbury Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge United Kingdom - Department of Molecular, Cell, and Developmental Biology, UCLA, Los Angeles, USA
- Schorderet, Martine Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Reinhardt, Didier Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Kuhlemeier, Cris Institute of Plant Sciences, University of Bern, Switzerland
-
01.12.2017
Published in:
- The Plant Cell. - 2017, vol. 29, no. 12, p. 2959–2973
English
How complex developmental-genetic networks are translated into organs with specific 3D shapes remains an open question. This question is particularly challenging because the elaboration of specific shapes is in essence a question of mechanics. In plants, this means how the genetic circuitry affects the cell wall. The mechanical properties of the wall and their spatial variation are the key factors controlling morphogenesis in plants. However, these properties are difficult to measure and investigating their relation to genetic regulation is particularly challenging. To measure spatial variation of mechanical properties, one must determine the deformation of a tissue in response to a known force with cellular resolution. Here, we present an automated confocal micro-extensometer (ACME), which greatly expands the scope of existing methods for measuring mechanical properties. Unlike classical extensometers, ACME is mounted on a confocal microscope and uses confocal images to compute the deformation of the tissue directly from biological markers, thus providing 3D cellular scale information and improved accuracy. Additionally, ACME is suitable for measuring the mechanical responses in live tissue. As a proof of concept, we demonstrate that the plant hormone gibberellic acid induces a spatial gradient in mechanical properties along the length of the Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyl.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Département de Biologie
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Biological sciences
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 306710
- DOI 10.1105/tpc.17.00753
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/306358
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 126
File downloads:
- pdf: 257
- Supplementary material: 175