Valproate induces the unfolded protein response by increasing ceramide levels
- Jadhav, Shyamalagauri Department of Biological Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan USA
- Russo, Sarah Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, USA - Ralph H. Johnson Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Charleston, South Carolina, USA
- Cottier, Stéphanie Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Schneiter, Roger Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Cowart, Ashley Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, USA - Ralph H. Johnson Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Charleston, South Carolina, USA
- Greenberg, Miriam L. Department of Biological Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan USA
-
14.10.2016
Published in:
- Journal of Biological Chemistry. - 2016, vol. 291, no. 42, p. 22253–22261
English
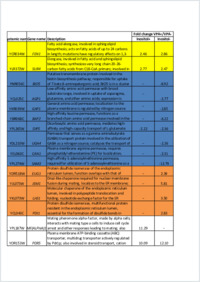
Bipolar disorder (BD), which is characterized by depression and mania, affects 1–2% of the world population. Current treatments are effective in only 40–60% of cases and cause severe side effects. Valproate (VPA) is one of the most widely used drugs for the treatment of BD, but the therapeutic mechanism of action of this drug is not understood. This knowledge gap has hampered the development of effective treatments. To identify candidate pathways affected by VPA, we performed a genome- wide expression analysis in yeast cells grown in the presence or absence of the drug. VPA caused up-regulation of FEN1 and SUR4, encoding fatty acid elongases that catalyze the synthesis of very long chain fatty acids (C24 to C26) required for ceramide synthesis. Interestingly, fen1Δ and sur4Δ mutants exhibited VPA sensitivity. In agreement with increased fatty acid elongase gene expression, VPA increased levels of phytoceramide, especially those containing C24–C26 fatty acids. Consistent with an increase in ceramide, VPA decreased the expression of amino acid transporters, increased the expression of ER chaperones, and activated the unfolded protein response element (UPRE), suggesting that VPA induces the UPR pathway. These effects were rescued by supplementation of inositol and similarly observed in inositol-starved ino1Δ cells. Starvation of ino1Δ cells increased expression of FEN1 and SUR4, increased ceramide levels, decreased expression of nutrient transporters, and induced the UPR. These findings suggest that VPA-mediated inositol depletion induces the UPR by increasing the de novo synthesis of ceramide.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Département de Biologie
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Biological sciences
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 278438
- DOI 10.1074/jbc.M116.752634
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/305215
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 104
File downloads:
- Supplementary material: 163
- Fichier principal: 118