Infected erythrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles alter vascular function via regulatory Ago2-miRNA complexes in malaria
- Mantel, Pierre-Yves Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA - Department ofMedicine, Unit of Anatomy, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Hjelmqvist, Daisy Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Walch, Michael Department ofMedicine, Unit of Anatomy, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Kharoubi-Hess, Solange Department ofMedicine, Unit of Anatomy, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Nilsson, Sandra Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Ravel, Deepali Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Ribeiro, Marina Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Grüring, Christof Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Ma, Siyuan Department of Biostatistics, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health,Boston, USA
- Padmanabhan, Prasad Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Trachtenberg, Alexander Harvard Catalyst Laboratory for Innovative Translational Technologies, Harvard Medical School, Boston, USA
- Ankarklev, Johan Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Brancucci, Nicolas M. Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA - Wellcome Trust Center for Molecular Parasitology, University of Glasgow, UK
- Huttenhower, Curtis Department of Biostatistics, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health,Boston, USA
- Duraisingh, Manoj T. Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA
- Ghiran, Ionita Division of Allergy and Infection, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, USA
- Kuo, Winston P. Harvard Catalyst Laboratory for Innovative Translational Technologies, Harvard Medical School, Boston, USA - Predicine, Inc., Hayward, California, USA
- Filgueira, Luis Department ofMedicine, Unit of Anatomy, University of Fribourg, Switzerland
- Martinelli, Roberta Center for Vascular Biology Research, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, USA
- Marti, Matthias Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, USA - Wellcome Trust Center for Molecular Parasitology, University of Glasgow, UK
-
10.10.2016
Published in:
- Nature Communications. - 2016, vol. 7, p. 12727
English
Malaria remains one of the greatest public health challenges worldwide, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. The clinical outcome of individuals infected with Plasmodium falciparum parasites depends on many factors including host systemic inflammatory responses, parasite sequestration in tissues and vascular dysfunction. Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines promotes endothelial activation as well as recruitment and infiltration of inflammatory cells, which in turn triggers further endothelial cell activation and parasite sequestration. Inflammatory responses are triggered in part by bioactive parasite products such as hemozoin and infected red blood cell-derived extracellular vesicles (iRBC-derived EVs). Here we demonstrate that such EVs contain functional miRNA-Argonaute 2 complexes that are derived from the host RBC. Moreover, we show that EVs are efficiently internalized by endothelial cells, where the miRNA-Argonaute 2 complexes modulate target gene expression and barrier properties. Altogether, these findings provide a mechanistic link between EVs and vascular dysfunction during malaria infection.
- Faculty
- Faculté des sciences et de médecine
- Department
- Département de Médecine
- Language
-
- English
- Classification
- Biological sciences
- License
-
License undefined
- Identifiers
-
- RERO DOC 277738
- DOI 10.1038/ncomms12727
- Persistent URL
- https://folia.unifr.ch/unifr/documents/305212
Other files
Statistics
Document views: 120
File downloads:
- pdf: 309
- Supplementary material: Figures 1-6 and Supplementary Table 1: 132
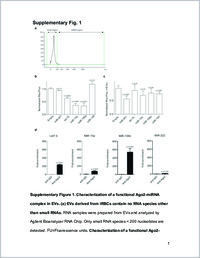
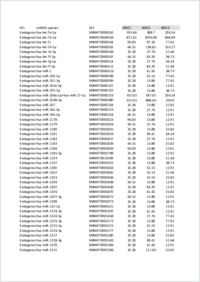
- Nanostring miRNA expression analysis. Shown are normalized nanostring miRNA expression values for the 800 human miRNAs. Data are normalized based on the highest 100 miRNAs expressed: 146